Postępowanie w przypadkach resorpcji wewnętrznej korzenia w zębach stałych
Management of internal root resorption on permanent teeth
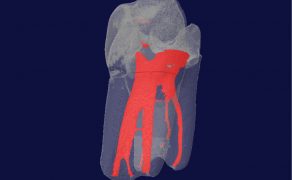
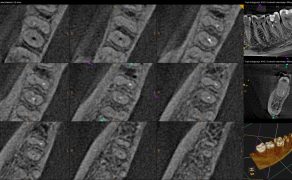
Resorption is a condition associated with either a physiologic or a pathologic process resulting in a loss of dentin, cementum, and/or bone [1]. Root resorption may occur after various injuries, including mechanical, chemical, or thermal injury. Generally, it can be classified as internal or external root resorption. This review concerns only the internal root resorption (IRR) on permanent tooth, focusing on therapeutic options depending on the diagnosis. Internal resorption is an inflammatory process initiated within the pulp space with loss of dentin and possible invasion of the cementum [1]. Resorption phenomena have been described for many years [2]. Most of the articles on this subject focuses on external root resorptions [3], while the internal resorptions also represent a challenge for the practitioner [4]. The diagnosis of these lesions is difficult to establish and the conventional X-ray is often inadequate. Internal root radiolucencies are not detectable on radiographs at their early stages, when they are small, or because of limitations of this 2-dimensional method. Cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) is a more powerful tool which allows an earlier and more accurate diagnosis of these lesions [5]. At the same time, new materials are offered to induce a remineralization and healing [6]. The contribution of these new ways of imaging and these new materials allow an extension of the boundaries for the conservation of teeth [7].
[...]
którzy są subskrybentami naszego portalu.
i ciesz się dostępem do bazy merytorycznej wiedzy!