Sposoby trakcji podniebiennie zatrzymanych kłów szczęki – przegląd piśmiennictwa
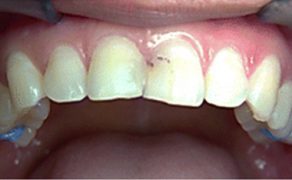
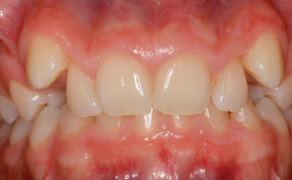
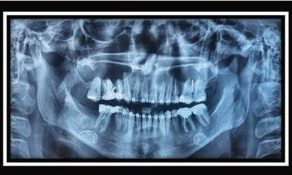
Tooth impaction is defined as a failed eruption of the permanent tooth with a completely formed root [1]. In the Polish orthodontic literature there is an extra criterium – an impacted tooths eruption into the oral cavity has to be delayed by a minimum of two years [2]. Maxillary canines are the second most frequent impacted teeth, after the third molars [1]. Impacted upper canines affect approximately 2% of the population and are twice as common in females as in males [3]. The ratio is even much higher in orthodontic patients – 23.5% [4].
Upper canines can be impacted palatally, buccally or centrally in line with the dental arch [5]. According to Ericson and Kurol, the ratio of palatally impacted canines to buccally impacted canines is 85% to 15% [6].
There are different approaches and treatment strategies for impacted maxillary canines described in the literature. They include:
- extraction of the primary canine, allowing spontaneous eruption of the impacted permanent tooth,
- extraction of impacted canine followed by implant placement or other prostethic replacement on the site or orthodontic closure of the space,
- autotransplantation of impacted canine,
- orthodontic traction of impacted canine, with or without the need for previous surgical exposure.
Early diagnosis and interceptive [...]

którzy są subskrybentami naszego portalu.
i ciesz się dostępem do bazy merytorycznej wiedzy!