Czynniki wpływające na stan tkanek okołowierzchołkowych zębów z wypełnionymi kanałami korzeniowymi u pacjentów leczonych przez studentów stomatologii – analiza przekrojowa
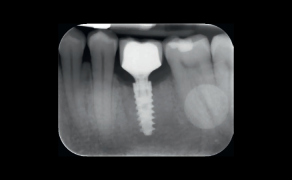
A periapical radiograph of each patient was performed using ultraspeed film (Eastman Kodak Co., Rochester, NY) according to the bisector technique and aided by an intraoral positioner (Maquira Indústria de Produtos Odontológicos Ltda, Maringá, PR, Brazil). Three previously calibrated examiners assessed these radiographs and rated the quality of the coronal restorations, quality of the root canal fillings, and periapical status. Using a projector (Kodak, Ektagraphic Universal Slide Tray, Kodak Company, NY, USA), the radiographs were projected in a dark room with 6x magnification and individually assessed by three calibrated examiners.
The coronal restorations were classified as I: adequate when exhibiting a well-adapted restoration in the cervical region of the proximal surfaces and II: inadequate when exhibiting overcontour signs on the proximal surfaces, open margins, or recurrent carious lesions. The clinical and radiographic findings were associated with the final classification of the restorations.
The radiographic quality of the fillings was classified according to the apical extension, homogeneity, and taper [14] by considering the tooth as the sample unit. When the tooth had more than one root canal, the worst-quality root canal was considered. The apical edge was measured using an image projected in a grid pattern. The apical limit, homogeneity, and taper were subclassified in scores: 0 (accentuated deviation from normality), 1 (mild deviation from normality), and 2 (gold standard). Data on the external root morphology and on the initial root canal diameter were considered to [...]

którzy są subskrybentami naszego portalu.
i ciesz się dostępem do bazy merytorycznej wiedzy!