Pacjentka z zespołem dysplazji ektodermalnej – opis przypadku i propozycja leczenia protetycznego
Oral symptoms
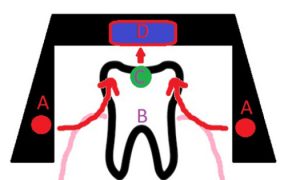
The disturbances within the mouth involve alveolar processes, teeth, and salivary glands. Alveolar processes are underdeveloped due to the lack of tooth germs or the presence of impacted teeth. Fewer salivary glands lead to dryness in the mouth, difficulty with swallowing, frequent infections of upper respiratory tract, and stomatitis. Due to decreased amounts of saliva, teeth are more prone to caries, and periodontal disorders are exacerbated. Dysfunctions of the tongue are also observed. Patients may speak in a rough and hoarse voice (3, 5-6, 8, 10).
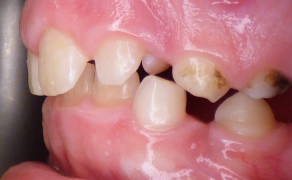
There is a partial or total absence of the germs of deciduous and permanent teeth, and their eruption is delayed. Based on the number of missing teeth, it can be described as hypodontia (missing individual teeth) or oligodontia (missing groups of teeth). The missing teeth are usually molars, second premolars, and lateral incisors in permanent dentition. Whereas the missing milk teeth are most commonly the incisors. The abnormalities are usually exacerbated in permanent teeth: severe cases show anodontia (a total lack of germs). Extraneous, congenitally impacted, and neonatal teeth are less common (1, 10-13). The mineralization of dental structures is impaired. The teeth are abnormally developed, including conical, stump-shaped, peg-shaped, and taurodontic teeth, as well as a decreased number of cusps in molars. Such abnormalities in tooth positions as diastemata, tremata, increased overbite, inclinations, rotations, infrapositions, transpositions, reinclusions, and even persistent deciduous teeth (usually heavily [...]

którzy są subskrybentami naszego portalu.
i ciesz się dostępem do bazy merytorycznej wiedzy!